Table of Contents
Fram2, the first crewed mission into a polar orbit of the Earth, left Earth on April 1st. After almost four days in orbit and completing fifty-five laps around the planet, the mission aboard Crew Dragon splashed down off the coast of California.
Following the splashdown and retrieval of Crew Dragon onboard a SpaceX recovery ship, the four crew members exited the spacecraft unassisted. A first for a Crew Dragon crew, and something not performed after the flight of a U.S. vehicle since the retirement of the Space Shuttle.
The Fram2 mission, named after the historic Norwegian exploration vessel Fram, had a crew of four onboard. Mission Commander Chun Wang funded the mission, Vehicle Commander Jannicke Mikkelsen was in command of Crew Dragon, along with Pilot Rabea Rogge, and Eric Philips was the Mission Specialist and Medical Officer. All four crew members were making their first trip to space.
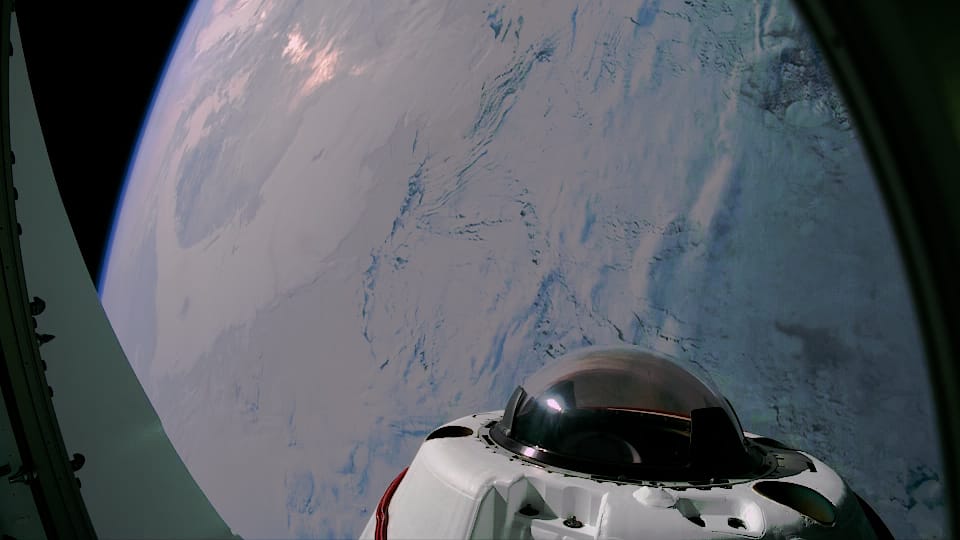
As the first crewed mission over the Earth's poles, many stunning views were shared.
First views of Earth's polar regions from Dragon pic.twitter.com/3taP34zCeN
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) April 1, 2025
Video from outside Crew Dragon, from its docking port cover, of the Earth's poles, via SpaceX on Twitter.
Hello, Antarctica.
— Chun (@satofishi) April 2, 2025
Unlike previously anticipated, from 460 km above, it is only pure white, no human activity is visible. pic.twitter.com/i7JawFYzW2
Views of Antarctica as seen during the Fram2 mission, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
Timelapse from Antarctica to the Arctic. pic.twitter.com/B3qZzNPBzB
— Chun (@satofishi) April 3, 2025
Earth seen in daylight from orbit during the Fram2 mission, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
Flight Day 3 pic.twitter.com/vLlbAKIOvl
— Chun (@satofishi) April 3, 2025
Views of Earth seen on the third day of the Fram2 mission, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
Flying over our launch site. pic.twitter.com/eHatUsOJ20
— Chun (@satofishi) April 3, 2025
Cape Canaveral, Florida, seen by Fram2 from orbit, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
I promised Svalbard I would wave to everyone there when I flew over them! Hi Svalbard 👋 and particular thank you to our auroral scientists and photographers #SolarMaxMission for participating in #Fram2 pic.twitter.com/12KqrnCsGM
— Jannicke Mikkelsen (@astro_jannicke) April 4, 2025
Svalbard as seen from orbit, via Jannicke Mikkelsen on Twitter.
Flight Day 4
— Chun (@satofishi) April 4, 2025
I woke up early and watched the launch of Starlink Group 11-13 on YouTube. Shortly after, SpaceX contacted us and informed us that we would be flying over Mongolia during the second stage deorbit burn. We opened the cupola and tried to observe the event, but had no… pic.twitter.com/OyOlShGYLP
Earth seen during the fourth and final day of the Fram2 mission, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
Deorbit, Draco style. pic.twitter.com/Rv3lKomOqB
— Chun (@satofishi) April 4, 2025
Crew Dragon deorbiting the Fram2 mission with Earth passing outside, via Chun Wang on Twitter.
During their time in orbit, the crew conducted the world's first X-ray in orbit on a human. Alongside that, other experiments performed were exercise studies to maintain muscle and skeletal mass, along with growing mushrooms in microgravity.
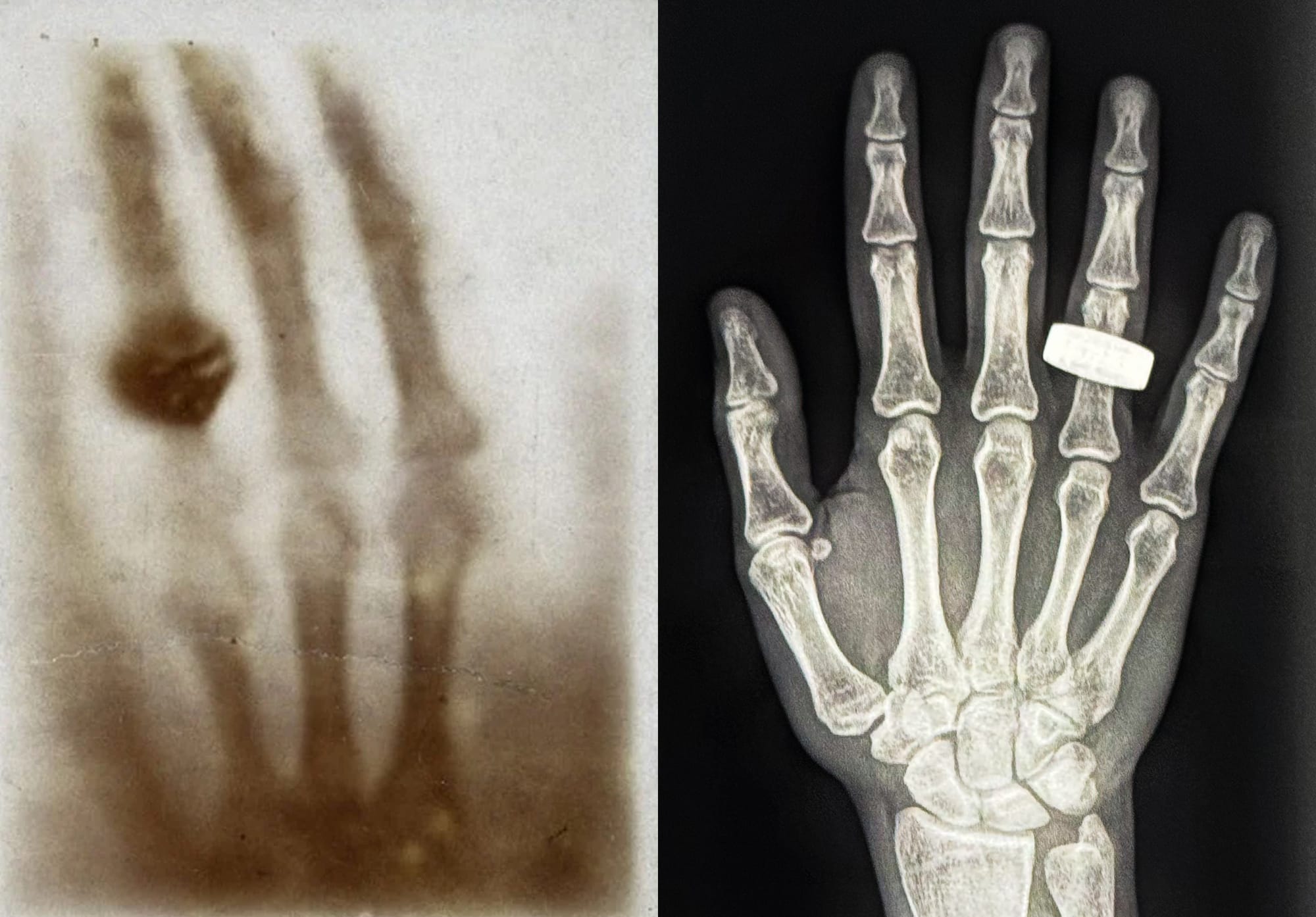
A full list of the experiments flown are:
- SpaceXray to capture the first human X-rays in space, paving the way for new clinical and research advancements.
- Egress to assess astronauts' ability to safely configure and exit the lander after short and long missions.
- BFR Study to test blood flow restriction exercise systems in Dragon to help maintain muscle and bone health on long missions.
- Mission MushVroom to grow oyster mushrooms in space to support astronaut nutrition and sustainable agriculture.
- Sleep Study using Oura Rings to track sleep and stress patterns before, during, and after spaceflight to improve astronaut recovery.
- Hyperfine MRI Study to image astronauts immediately upon return to better understand spaceflight’s effects on the brain.
- Diabetes Study to validate glucose monitoring in space to ensure safe, accurate care for diabetic astronauts.
- Women’s Health Study to use Hormona to analyze the effects of space on female reproductive hormones.
- Space THAL to examine how microgravity affects blood health and space-induced anemia.
- Motion Sickness Study to measure severity and duration of space motion sickness across gravity transitions.
- Bone Health Study to track bone microstructure changes to predict long-term skeletal impacts of Mars missions.
Additionally, the mission hosted a ham radio competition for high school and university students. The competition had images transmitted from the spacecraft but mixed into four separate pieces, requiring teams to tune in to multiple passes.






